| Macroscopic characters | shape | Applanate to ungulate; sessile |
| size | Up to 30 cm wide |
| texture | Woody |
| pileus | Yellowish brown; finely tomentose; becoming black with age; deeply rimose; glabrous |
| stipe | None |
| context | Light reddish brown; azonate; up to 2.5 cm thick |
| pore surface | Yellowish to reddish brown |
| pores | Circular; 7-8 per mm |
| tube layer(s) | Concolorous and continuous with context; distinctly stratified; woody; up to 3 mm thick |
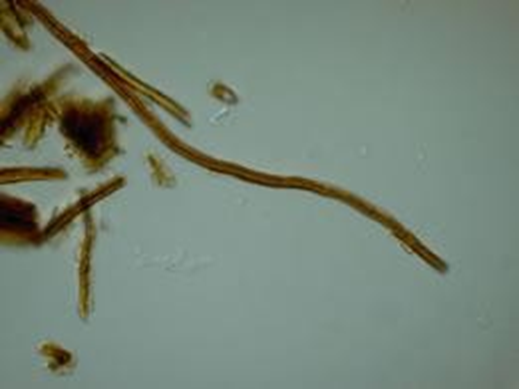
| Microscopic characters | hyphal system | Dimitic |
| clamp connections | None |
| sterile elements | None |
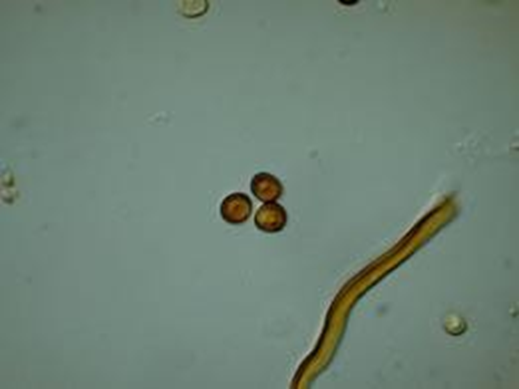
| basidiospores | Ovoid to subglobose; appearing flattened on one side; reddish- brown; smooth; 5-6 x 4.5-5 µm |
| Habitat characters | substrate/host | Chiefly on living or dead Robinia spp., esp. black locust (R. pseudoacacia); reported on a few other hardwood |
| seasonality | Perennial |
| type of decay | White rot of heartwood of living black locusts |
| range | Throughout eastern United States; in southwestern United States |
| Notes | Phellinus robineae is apparently present in the southwestern United States wherever Robinia neomexicana grows |
| References | Gilbertson & Ryvarden, 1987; Grand & Vernia, 2004A; Overholts, 1953 |