| Macroscopic characters | shape | Dimidiate |
| size | Up to 7 x 12 x 3 cm |
| texture | Tough-fibrous when young; brittle with age |
| pileus | Solitary or imbricate; dark yellowish brown; tomentose to glabrous; often rugose |
| stipe | N/A |
| context | Bright yellowish brown; zonate |
| pore surface | Dark purplish brown |
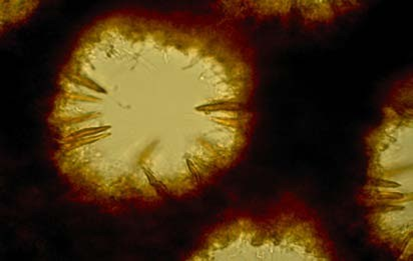
| pores | Circular; 6-8 per mm |
| tube layer(s) | White stuffed; up to 1 cm thick |
| Microscopic characters | hyphal system | Dimitic |
| clamp connections | N/A |
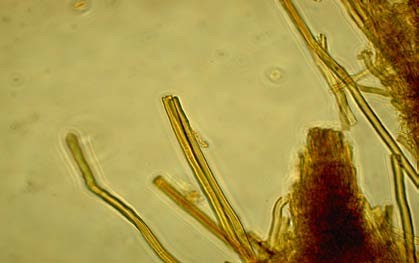
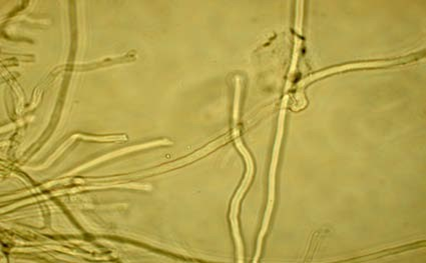
| sterile elements | Setae abundant; subulate; sharp; thick-walled; dark brown in KOH |
| basidiospores | Ellipsoid to ovoid; hyaline, smooth; 4-5 x 3-3.5 um |
| Habitat characters | substrate/host | Living and dead hardwoods in many genera; generally common on oaks; rarely on conifers |
| seasonality | Annual or perennial |
| type of decay | Uniform white rot of dead woods of hardwoods and a heart rot of living trees |
| range | Throughout the eastern United States and into southeastern Canada; in the Southwest and Pacific Coast regions; rare in the central rocky mountains |
| Notes | Purplish color of pore surface is very characteristic |
| References | Overholts, 1953; Gilbertson & Ryvarden, 1986. Grand & Vernia; 2000, 2004 |