| Macroscopic characters | shape | Applanate; dimidiate to flabelliform |
| size | Up to 20 x 30 x 7 cm; single or in clusters |
| texture | Smooth to irregularly rugose and wrinkled |
| pileus | Reddish brown to mahogany or almost black; highly varnished laccate crust |
| stipe | Usually lateral; often vertical and well developed; up to 5 cm wide and 9 cm long; continuous and concolorus with pileus |
| context | Cream colored to pale buff; azonate; spongy to tough; up to 5 cm thick |
| pore surface | Cream colored when fresh; bruising and drying ochraceous to light brown |
| pores | Circular to angular; 5-6 per mm |
| tube layer(s) | Pale purplish brown; up to 1.5 cm thick |
| Microscopic characters | hyphal system | Trimitic: generative, skeletal and binding hyphae |
| clamp connections | Present on generative hyphae |
| sterile elements | N/A |
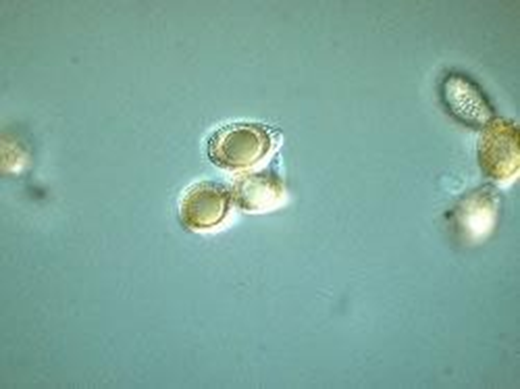
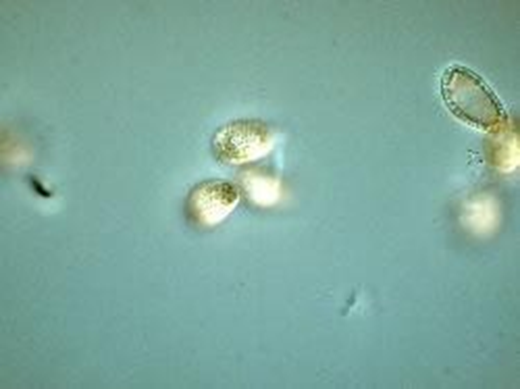
| basidiospores | Ellipsoid; truncate at the apex; pale brown in KOH; wall two layered with interwall pillars between layers; outer wall with pronounced depressions; 13-15 x 7.5-8.5 um |
| Habitat characters | substrate/host | Living and dead conifers in several genera; almost exclusively on Tsuga (hemlock) in eastern U.S. |
| seasonality | Annual |
| type of decay | White butt rot of heartwood in living and dead conifers |
| range | Widely distributed in eastern forests from Canada to the Gulf Coast region, also common in the Southwest. |
| Notes | Apparently restricted to conifers |
| References | Overholts, 1953; Gilbertson & Ryvarden, 1986; Grand & Vernia,2005B |