| Macroscopic characters | shape | Stipitate; imbricate in large clusters, often in a rosette form |
| size | Large, up to 25 x 15 x 3 cm |
| texture | Tought to corky |
| pileus | Tan to yellowish; finely tomentose or appressed-strigose to glabrous |
| stipe | Branched; lateral; up to 8 cm thick |
| context | Pale buff; corky |
| pore surface | Tan |
| pores | Circular to angular; 1-2 per mm |
| tube layer(s) | Concolorous and continuous with context; decurrent on stipe; up to 2 cm thick |
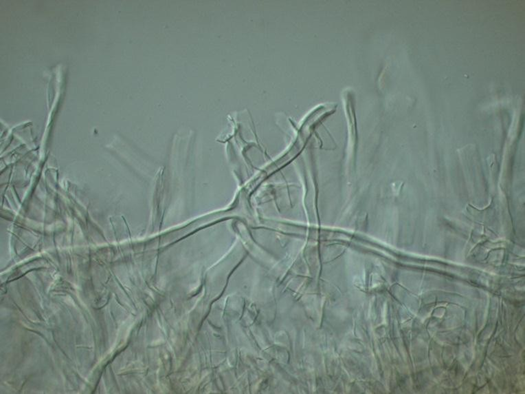
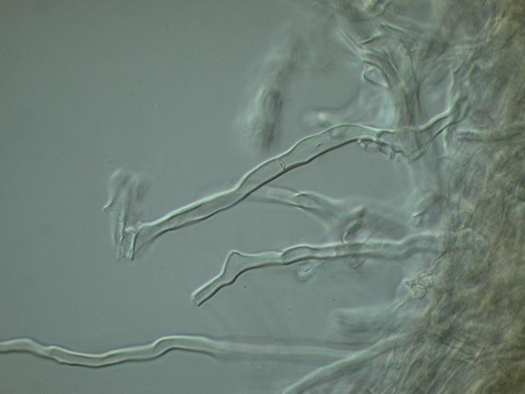
| Microscopic characters | hyphal system | Dimitic; skeletal hyphae very thick |
| clamp connections | None |
| sterile elements | None |
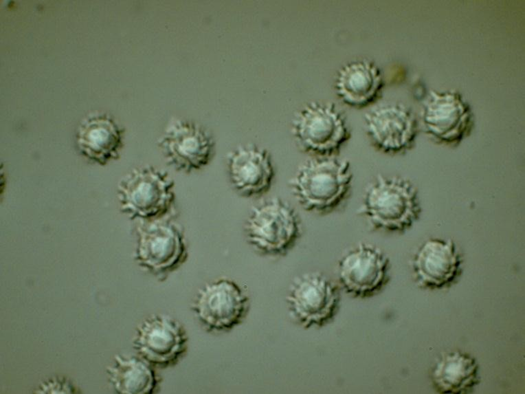
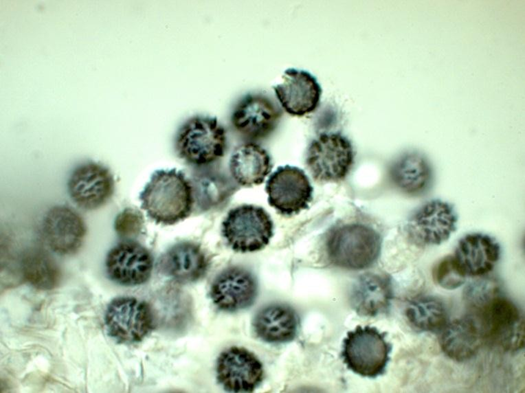
| basidiospores | Globose to subglobose; hyaline; ornamented with short; irregularly arranged; strongly amyloid ridges; 7-9 x 6-8 µm |
| Habitat characters | substrate/host | Fruiting from the base of hardwood trees and stumps; particularly common Quercus and Castanea |
| seasonality | Annual |
| type of decay | White stringy rot of the heartwood in roots and butts of living hardwoods; continuing decay in dead trees and stumps |
| range | Hardwood forest regions of eastern North America |
| Notes | Developing from an underground sclerotium |
| References | Gilberrtsin & Ryvarden, 1986; Grand & Vernia, 2007; Overholts, 1953 |